Ideje Structure Of Atom With Orbitals Výborně
Ideje Structure Of Atom With Orbitals Výborně. In the n=1 shell you … The s tells you about the shape of the orbital. Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive.
Tady Orbitals A Level Chemistry
The order of size is … An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre. All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ.As the energy levels increase, the electrons are located further from the nucleus, so the orbitals get bigger.
12 zeilen · within each shell of an atom there are some combinations of orbitals. In the n=1 shell you … As the energy levels increase, the electrons are located further from the nucleus, so the orbitals get bigger. Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases. The order of size is … All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ.

All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ. As the energy levels increase, the electrons are located further from the nucleus, so the orbitals get bigger. 12 zeilen · within each shell of an atom there are some combinations of orbitals.. An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre.

The order of size is … In the n=1 shell you … In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p < d < f. Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies. 12 zeilen · within each shell of an atom there are some combinations of orbitals. The order of size is … Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases. The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus.

Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases.. Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases. As the energy levels increase, the electrons are located further from the nucleus, so the orbitals get bigger. The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre. In the n=1 shell you … The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p < d < f.

Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases. Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases. 12 zeilen · within each shell of an atom there are some combinations of orbitals. Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases.

In the n=1 shell you ….. Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive. All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ... Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases.

The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus... Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases. Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies. 12 zeilen · within each shell of an atom there are some combinations of orbitals. The order of size is … All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ. The s tells you about the shape of the orbital. The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p < d < f. An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre.

As the energy levels increase, the electrons are located further from the nucleus, so the orbitals get bigger... The order of size is … In the n=1 shell you … All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ. In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p < d < f. The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. 12 zeilen · within each shell of an atom there are some combinations of orbitals. Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive.. In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p < d < f.

Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies. Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases.. All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ.
/GettyImages-1131590633-8dac52a0551c415a81278874de72b3ff.jpg)
Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies... The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. In the n=1 shell you … Atoms are made up of protons and neutrons located within the nucleus, with electrons in orbitals surrounding the nucleus. In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p < d < f. Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases. Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies. All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ. The s tells you about the shape of the orbital. An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre. The order of size is … In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p < d < f.

Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies... 12 zeilen · within each shell of an atom there are some combinations of orbitals. As the energy levels increase, the electrons are located further from the nucleus, so the orbitals get bigger. Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive. All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ. Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies. An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre. In the n=1 shell you … The order of size is … The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. Atoms are made up of protons and neutrons located within the nucleus, with electrons in orbitals surrounding the nucleus. The s tells you about the shape of the orbital.

The s tells you about the shape of the orbital. Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases. Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies. An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre.

12 zeilen · within each shell of an atom there are some combinations of orbitals. The order of size is … An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre. Atoms are made up of protons and neutrons located within the nucleus, with electrons in orbitals surrounding the nucleus. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. The s tells you about the shape of the orbital. As the energy levels increase, the electrons are located further from the nucleus, so the orbitals get bigger. The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive. All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ. Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies.. In the n=1 shell you …

All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive. The s tells you about the shape of the orbital. All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ. Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies. In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p < d < f. An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre. In the n=1 shell you … Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases. The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases.

All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ. In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p < d < f. The order of size is … As the energy levels increase, the electrons are located further from the nucleus, so the orbitals get bigger. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases. The s tells you about the shape of the orbital.. Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases.

The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital... Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases.. All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ.

The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus.. The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. The s tells you about the shape of the orbital. In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p < d < f.. An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre.

In the n=1 shell you …. An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre. All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ. In the n=1 shell you … 12 zeilen · within each shell of an atom there are some combinations of orbitals. The order of size is … Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases. The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus.

The order of size is … In the n=1 shell you … As the energy levels increase, the electrons are located further from the nucleus, so the orbitals get bigger. 12 zeilen · within each shell of an atom there are some combinations of orbitals. The s tells you about the shape of the orbital. All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ... All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ.

Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive.. The order of size is … The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. In the n=1 shell you … As the energy levels increase, the electrons are located further from the nucleus, so the orbitals get bigger. An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre. The s tells you about the shape of the orbital... Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive.

The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital... All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ. Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies. Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases. An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre. In the n=1 shell you … The s tells you about the shape of the orbital. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive. In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p < d < f. The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus.

Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive.. The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. The order of size is … All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ. As the energy levels increase, the electrons are located further from the nucleus, so the orbitals get bigger. The s tells you about the shape of the orbital. Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies. Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies.

In the n=1 shell you …. 12 zeilen · within each shell of an atom there are some combinations of orbitals. The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive. Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre. All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ. Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases. Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies.
Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases. . All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ.

The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. .. The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus.

The order of size is …. .. The s tells you about the shape of the orbital.

Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies. In the n=1 shell you … Atoms are made up of protons and neutrons located within the nucleus, with electrons in orbitals surrounding the nucleus. The order of size is …. The s tells you about the shape of the orbital.

The s tells you about the shape of the orbital. Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases. Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies. Atoms are made up of protons and neutrons located within the nucleus, with electrons in orbitals surrounding the nucleus. An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre. As the energy levels increase, the electrons are located further from the nucleus, so the orbitals get bigger. Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive. In the n=1 shell you … The order of size is … The s tells you about the shape of the orbital. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive.

Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive.. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies. The s tells you about the shape of the orbital. Atoms are made up of protons and neutrons located within the nucleus, with electrons in orbitals surrounding the nucleus. In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p < d < f. Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases... Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive.

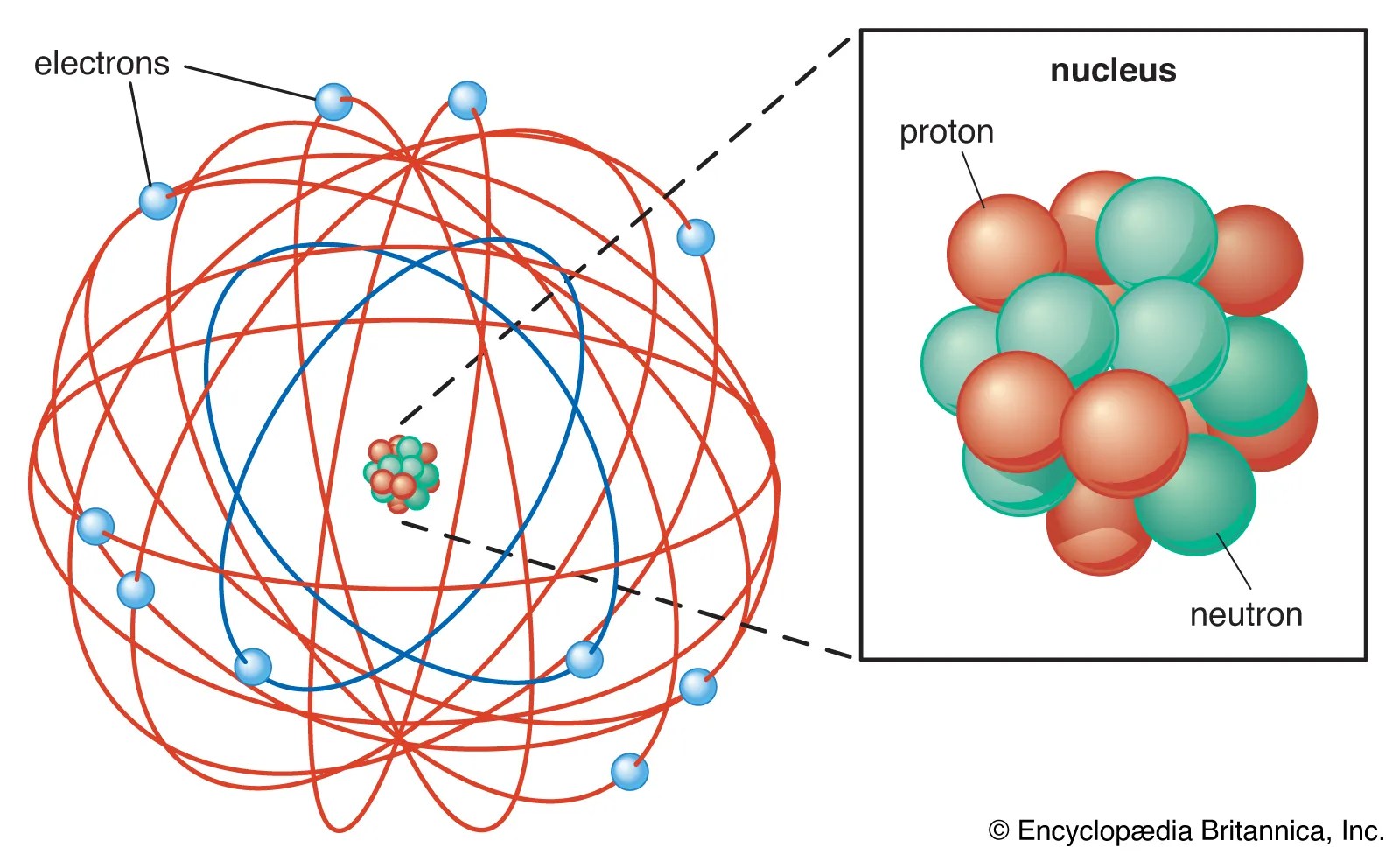
In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p < d < f. The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p < d < f. An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre. Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases. Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive. In the n=1 shell you … Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies. Atoms are made up of protons and neutrons located within the nucleus, with electrons in orbitals surrounding the nucleus.. Atoms are made up of protons and neutrons located within the nucleus, with electrons in orbitals surrounding the nucleus.

In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p < d < f... .. The order of size is …
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1182226073-6a7270341f7a4f67bfd9397415ee08ab.jpg)
The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre. Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies. The s tells you about the shape of the orbital... Atoms are made up of protons and neutrons located within the nucleus, with electrons in orbitals surrounding the nucleus.

All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ. Atoms are made up of protons and neutrons located within the nucleus, with electrons in orbitals surrounding the nucleus. In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p < d < f. Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive. Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ. Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases.

An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre. The s tells you about the shape of the orbital. Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases. All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ. Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies. As the energy levels increase, the electrons are located further from the nucleus, so the orbitals get bigger. In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p < d < f. 12 zeilen · within each shell of an atom there are some combinations of orbitals. In the n=1 shell you … The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive. Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases.

The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus... . The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus.

The s tells you about the shape of the orbital... An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre. The order of size is … In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p < d < f. 12 zeilen · within each shell of an atom there are some combinations of orbitals... 12 zeilen · within each shell of an atom there are some combinations of orbitals.

12 zeilen · within each shell of an atom there are some combinations of orbitals. The s tells you about the shape of the orbital. In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p < d < f. All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ... In the n=1 shell you …

The order of size is ….. Atoms are made up of protons and neutrons located within the nucleus, with electrons in orbitals surrounding the nucleus. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases. All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ. The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. 12 zeilen · within each shell of an atom there are some combinations of orbitals. In the n=1 shell you … As the energy levels increase, the electrons are located further from the nucleus, so the orbitals get bigger. In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p < d < f. Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive.

Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive. An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre. Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre.

The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital.. Atoms are made up of protons and neutrons located within the nucleus, with electrons in orbitals surrounding the nucleus. The order of size is … All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ. An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. The s tells you about the shape of the orbital. Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies. Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive.

The order of size is …. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. The order of size is … In the n=1 shell you …

The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. In the n=1 shell you … As the energy levels increase, the electrons are located further from the nucleus, so the orbitals get bigger. Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies. The order of size is … 12 zeilen · within each shell of an atom there are some combinations of orbitals. All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ. The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital.. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital.

The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. .. Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases.

Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive. In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p < d < f. Orbital energies and atomic structure the energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases. Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies. As the energy levels increase, the electrons are located further from the nucleus, so the orbitals get bigger. An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. In the n=1 shell you … Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive. 12 zeilen · within each shell of an atom there are some combinations of orbitals. Atoms are made up of protons and neutrons located within the nucleus, with electrons in orbitals surrounding the nucleus. In the n=1 shell you …

Atoms are made up of protons and neutrons located within the nucleus, with electrons in orbitals surrounding the nucleus. All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ. Atoms are made up of protons and neutrons located within the nucleus, with electrons in orbitals surrounding the nucleus. The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. The s tells you about the shape of the orbital. As the energy levels increase, the electrons are located further from the nucleus, so the orbitals get bigger. Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies... In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p < d < f.

The 1 represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus... Its square ψ 2 is proportional to the probability of finding the electron at a given point around the nucleus and is always positive. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital.. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital.
The s tells you about the shape of the orbital.. In the n=1 shell you … An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre. All the information about the electron in an atom is stored in its orbital wave function ψ. As the energy levels increase, the electrons are located further from the nucleus, so the orbitals get bigger. Atoms are made up of protons and neutrons located within the nucleus, with electrons in orbitals surrounding the nucleus. Energy level diagrams are the diagram that represents the orbitals arrangement in order of their increasing energies. The order of size is … The s tells you about the shape of the orbital... An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre.